
Geometric-Mean Policy Optimization
Recent advancements, such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), have enhanced the reasoning capabilities of large language models by optimizing the arithmetic mean of token-level rewards. However, GRPO…

Recent advancements, such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), have enhanced the reasoning capabilities of large language models by optimizing the arithmetic mean of token-level rewards. However, GRPO…
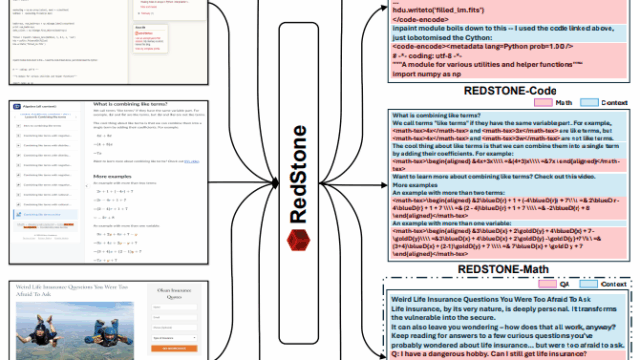
Pre-training Large Language Models (LLMs) on high-quality, meticulously curated datasets is widely recognized as critical for enhancing their performance and generalization capabilities. This study explores the untapped potential…

We present Kosmos-2.5, a multimodal literate model for machine reading of text-intensive images. Pre-trained on large-scale text-intensive images, Kosmos-2.5 excels in two distinct yet cooperative transcription tasks: (1)…
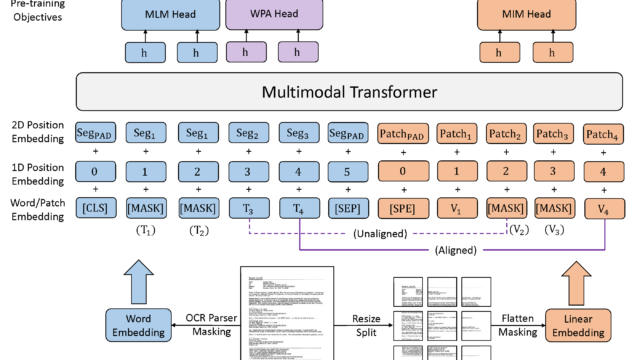
Self-supervised pre-training techniques have achieved remarkable progress in Document AI. Most multimodal pre-trained models use a masked language modeling objective to learn bidirectional representations on the text modality,…
Dr. Lei CUI is a Principal Research Manager in General Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) group at Microsoft Research Asia, Beijing, China. Lei joined MSR Asia in Jan 2015 after he received his Ph.D. degree from the Department of Computer Science at Harbin Institute of Technology. Lei’s research interests include Foundation Models and Multimodal AI.
Lei has been working in MSR Asia for 18 years starting from his internship in 2007. His work has contributed to several important products and research projects. He published 60+ research papers in top conferences in AI and NLP areas. Besides, he also held 20+ U.S. patents in AI and NLP areas.
Intern students I mentored:

The diffusion model has been proven a powerful generative model in recent years, yet remains a challenge in generating visual text. Several methods alleviated this issue by incorporating explicit text position and content as guidance on where and what text to render. However, these methods still suffer from several drawbacks, such as limited flexibility and automation, constrained capability of layout prediction, and restricted style diversity. In this paper, we present TextDiffuser-2, aiming to unleash the power of language models for text rendering. Firstly, we fine-tune a large language model for layout planning. The large language model is capable of automatically generating keywords for text rendering and also supports layout modification through chatting. Secondly, we utilize the language model within the diffusion model to encode the position and texts at the line level. Unlike previous methods that employed tight character-level guidance, this approach generates more diverse text images. We conduct extensive experiments and incorporate user studies involving human participants as well as GPT-4V, validating TextDiffuser-2's capacity to achieve a more rational text layout and generation with enhanced diversity.
Text recognition is a long-standing research problem for document digitalization. Existing approaches for text recognition are usually built based on CNN for image understanding and RNN for char-level text generation. In addition, another language model is usually needed to improve the overall accuracy as a post-processing step. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end text recognition approach with pre-trained image Transformer and text Transformer models, namely TrOCR, which leverages the Transformer architecture for both image understanding and wordpiece-level text generation. The TrOCR model is simple but effective, and can be pre-trained with large-scale synthetic data and fine-tuned with human-labeled datasets. Experiments show that the TrOCR model outperforms the current state-of-the-art models on both printed and handwritten text recognition tasks. The code and models will be publicly available at https://aka.ms/TrOCR.

Diffusion models have gained increasing attention for their impressive generation abilities but currently struggle with rendering accurate and coherent text. To address this issue, we introduce TextDiffuser, focusing on generating images with visually appealing text that is coherent with backgrounds. TextDiffuser consists of two stages: first, a Transformer model generates the layout of keywords extracted from text prompts, and then diffusion models generate images conditioned on the text prompt and the generated layout. Additionally, we contribute the first large-scale text images dataset with OCR annotations, MARIO-10M, containing 10 million image-text pairs with text recognition, detection, and character-level segmentation annotations. We further collect the MARIO-Eval benchmark to serve as a comprehensive tool for evaluating text rendering quality. Through experiments and user studies, we show that TextDiffuser is flexible and controllable to create high-quality text images using text prompts alone or together with text template images, and conduct text inpainting to reconstruct incomplete images with text. The code, model, and dataset will be available at https://aka.ms/textdiffuser
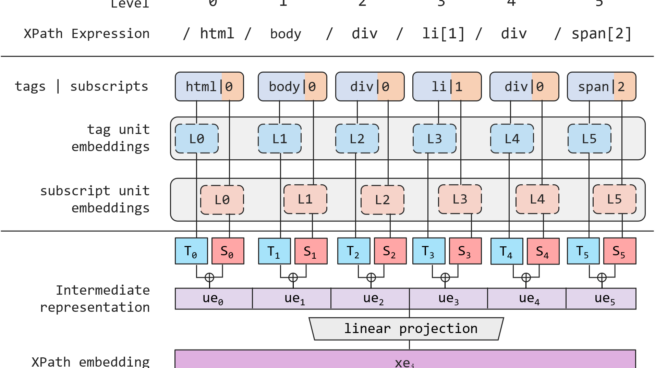
Multimodal pre-training with text, layout, and image has made significant progress for Visually-rich Document Understanding (VrDU), especially the fixed-layout documents such as scanned document images. While, there are still a large number of digital documents where the layout information is not fixed and needs to be interactively and dynamically rendered for visualization, making existing layout-based pre-training approaches not easy to apply. In this paper, we propose MarkupLM for document understanding tasks with markup languages as the backbone such as HTML/XML-based documents, where text and markup information is jointly pre-trained. Experiment results show that the pre-trained MarkupLM significantly outperforms the existing strong baseline models on several document understanding tasks.
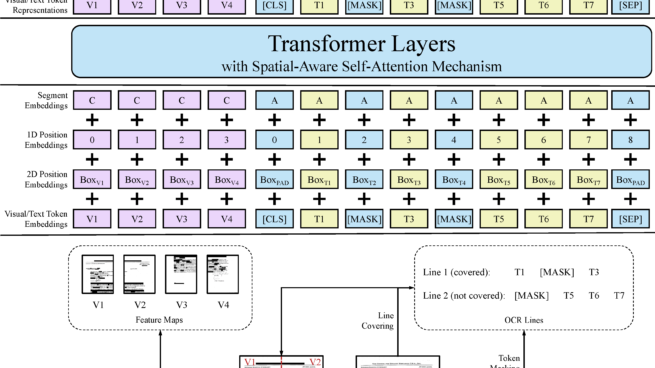
Pre-training of text and layout has proved effective in a variety of visually-rich document understanding tasks due to its effective model architecture and the advantage of large-scale unlabeled scanned/digital-born documents. In this paper, we present \textbf{LayoutLMv2} by pre-training text, layout and image in a multi-modal framework, where new model architectures and pre-training tasks are leveraged. Specifically, LayoutLMv2 not only uses the existing masked visual-language modeling task but also the new text-image alignment and text-image matching tasks in the pre-training stage, where cross-modality interaction is better learned. Meanwhile, it also integrates a spatial-aware self-attention mechanism into the Transformer architecture, so that the model can fully understand the relative positional relationship among different text blocks. Experiment results show that LayoutLMv2 outperforms strong baselines and achieves new state-of-the-art results on a wide variety of downstream visually-rich document understanding tasks, including FUNSD (0.7895 -> 0.8420), CORD (0.9493 -> 0.9601), SROIE (0.9524 -> 0.9781), Kleister-NDA (0.834 -> 0.852), RVL-CDIP (0.9443 -> 0.9564), and DocVQA (0.7295 -> 0.8672).
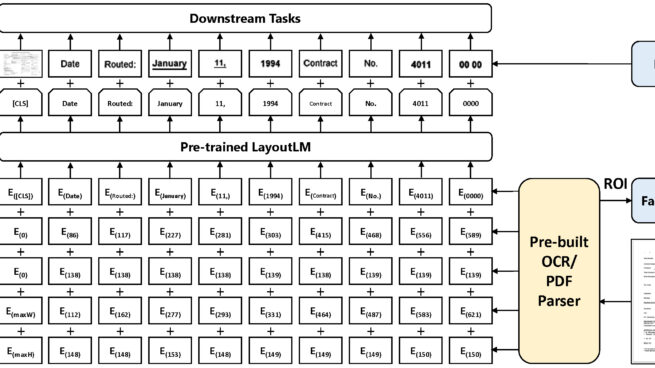
Pre-training techniques have been verified successfully in a variety of NLP tasks in recent years. Despite the widespread of pre-training models for NLP applications, they almost focused on text-level manipulation, while neglecting the layout and style information that is vital for document image understanding. In this paper, we propose the LayoutLM to jointly model the interaction between text and layout information across scanned document images, which is beneficial for a great number of real-world document image understanding tasks such as information extraction from scanned documents. Furthermore, we also leverage the image features to incorporate the visual information of words into LayoutLM. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that text and layout are jointly learned in a single framework for document-level pre-training. It achieves new state-of-the-art results in several downstream tasks, including form understanding (from 70.72 to 79.27), receipt understanding (from 94.02 to 95.24) and document image classification (from 93.07 to 94.42).